Projects | In Progress
Economic Modeling to Understand the Relationship Between Clinicians and Outcomes of Mechanically Ventilated Patients
Research Areas
Principal Investigator
PAIR Center Research Team
Topics
Overview
The one million Americans who undergo mechanical ventilation (MV) annually in intensive care units (ICUs) are at high risk for morbidity and mortality. Even after accounting for differences in acuity, variability exists in processes of care, patient outcomes, and resource utilization. We have shown that risk-adjusted outcomes of MV patients vary among physicians, and other studies have identified specific nurse and physician factors associated with patient outcomes, suggesting that clinicians contribute to this variability. However, MV patients are typically cared for by multiple clinicians in interprofessional teams, which has not been accounted for in these studies. Furthermore, measurement of effective team collaboration remains elusive. Understanding the contributions of individuals and teams would help to bridge this knowledge gap and inform efforts focused on team collaboration to reduce undue variability in MV patient care and outcomes. This study will rigorously evaluate of the contributions of clinicians and teams to mechanical ventilation (MV) patient outcomes, advance the science of team effectiveness, and evaluate new methods for performance measurement and outcomes research.
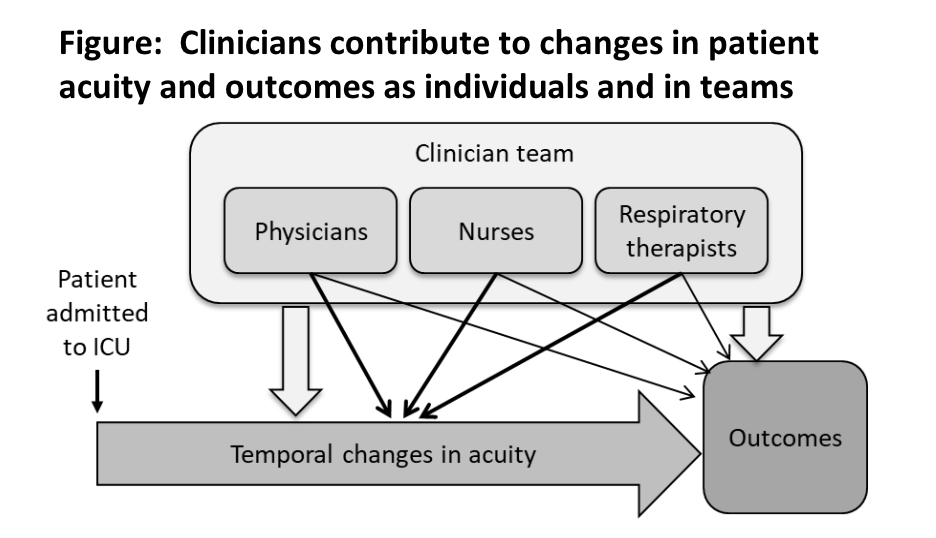
Diagram explaining how clinicians contribute to changes in patient severity of illness and outcomes as individuals and in teams
Partnering Health Systems
University of Pennsylvania Health System
Oregon Health and Science University
Sponsors
National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)





